AFFILIAZIONE
fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico
AUTORE PRINCIPALE
Dr. Crescenzi Anna
VALUTA IL CHALLENGE
GRUPPO DI LAVORO
Dr. Crescenzi Anna – fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico, roma
Dr. Verri Martina – fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico, roma
Dr. Taffon Chiara – fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico, roma
Dr. Stigliano Serena – fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico, roma
PhD Banchi Roberto – vivascope gmbh,, munich
Dr. Di Matteo Francesco Maria – fondazione policlinico universitario campus bio-medico, roma
AREA TEMATICA
Sanità digitale e telemedicina
ABSTRACT
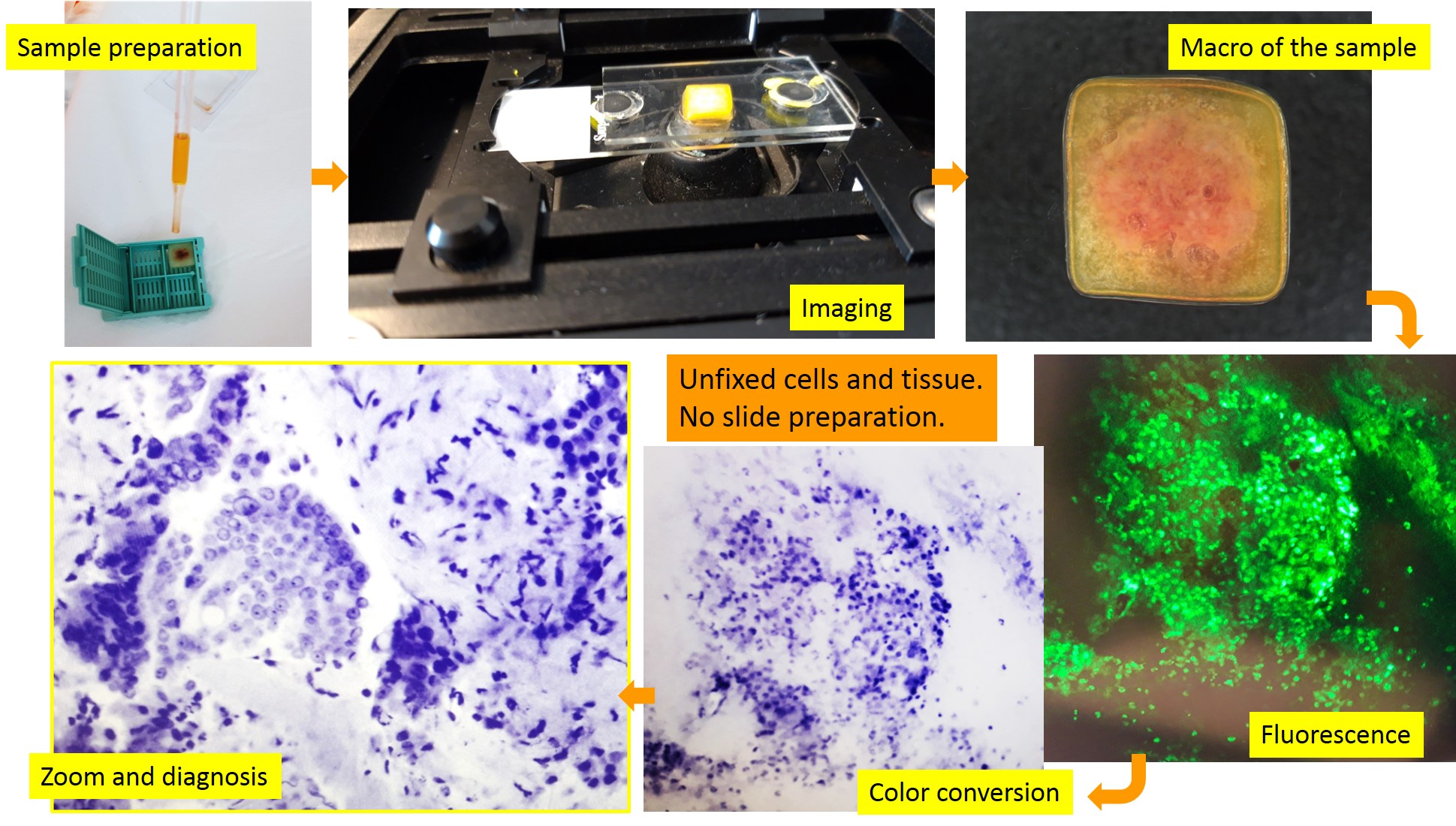
Modern medicine requires rapid diagnosis and accurate characterization of the pathology to provide the best therapeutic approach. Ex-vivo fluorescence confocal microscopes (FCMs) allow for fast microscopic assessment in the fresh state of the tissue with accuracy in the visualization of both cellular and architectural details. This technique is able to produce microscopic digital images in real time directly from the biological specimens, without preparation of the physical histological slide. It is known as instant digital pathology. This technique is rapidly emerging for real-time microscopic assessment of resection margins in various fields of surgery such skin tumors, urological neoplasms, prostatic cancer and for immediate diagnosis in different organs such colon, prostate, thyroid. Our study was aimed to develop a consistent and reproducible protocol for submitting cellular material and micro-fragments of tissue from pancreatic EUS-FNB to instant digital pathology assessment. As secondary aim, we evaluate the performance of this approach by comparing sample adequacy assessment and diagnostic evaluation on these digital biopsies with their paired conventional histology. Ninety cases of EUS-FNB samples from solid pancreatic lesions were observed from April 2020 to September 2021 at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Campus Bio-Medico of Rome. All patients signed the informed consent. The protocol for sample preparation was developed using a polymeric matrix as specimens holder and by modulating the laser power and/or the incubation period of the specimen in the fluorescent solution (acridine orange), to obtain the best possible visualization of microscopic details. From the performance point of view, we find an accuracy of 97% and a positive predictive value of 99%. Patients with pancreatic lesions will benefit from immediate evidence of biopsy quality to avoid the occurrence of inadequate sampling. Clinicians will be able to start patients’ management at the time of the EUS-FNB without diagnostic delay. A collaboration between Physicians and Engineers is expected for extensive development of instant digital pathology for characterization of cell and tissue by ancillary techniques to improve quickness in targeted treatments. Finally, instant digital images are suitable for artificial intelligence approach skipping the current limits of traditional digital pathology such as staining variation and thickness variability.



